Linux Networking Course
History
*Arpanet
*switched network
*TCP/IP
*spread in the 90's
TCP/IP
What is a protocol
*strict procedure how things are done
*communication between layers
*clearly defined interfaces
*data encapsulation
*example
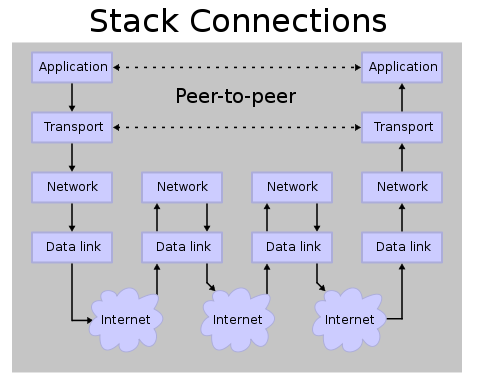
TCP/IP protocol
*Application
*Transport
*Network
*Physical / Data link
from wikipedia
Physical layer / Data link layer
*not much of a concern for us.
*different topologies (ethernet, wirless, DSL, modem etc)
*this is about the physical connection
*here the bits are shifted.
*how many Volt represent a 1, how many a 0
*ethernet address (HWaddr in Hex format)
Network layer
*IP ICMP
*IPv4 32bit written in dotted decimal notation
*65.212.180.178
*different classes
A starts with 0 B starts with 10 C starts with 110 D starts with 1110
*although outdated it roughly specifies the network and host part.
*Common now is the CIDR (Classless InterDomain Routing)
192.168.10.3/24
this actually stands for
11000000 10101000 00001010 00000011 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
private networks that are not routed
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix) 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix) 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix)
localhost 127.0.0.0/8
"network addresses" ending with 0
"broadcast addresses" ending with 255
routing
nat
configuration
Transport Layer
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
connectionless
media-streaming
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
makes sure every packet arrives
if it didn't arrive, it will request it again
ftp-data-transfer
*connections through ports
*well known ports can be found in /etc/services
~$ cat /etc/services # Network services, Internet style # # Note that it is presently the policy of IANA to assign a single well-known # port number for both TCP and UDP; hence, officially ports have two entries # even if the protocol doesn't support UDP operations. # # Updated from http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers and other # sources like http://www.freebsd.org/cgi/cvsweb.cgi/src/etc/services . # New ports will be added on request if they have been officially assigned # by IANA and used in the real-world or are needed by a debian package. # If you need a huge list of used numbers please install the nmap package. tcpmux 1/tcp # TCP port service multiplexer echo 7/tcp echo 7/udp discard 9/tcp sink null discard 9/udp sink null systat 11/tcp users daytime 13/tcp daytime 13/udp netstat 15/tcp qotd 17/tcp quote msp 18/tcp # message send protocol msp 18/udp chargen 19/tcp ttytst source chargen 19/udp ttytst source ftp-data 20/tcp ftp 21/tcp fsp 21/udp fspd ssh 22/tcp # SSH Remote Login Protocol ssh 22/udp telnet 23/tcp smtp 25/tcp mail time 37/tcp timserver time 37/udp timserver rlp 39/udp resource # resource location nameserver 42/tcp name # IEN 116 whois 43/tcp nicname tacacs 49/tcp # Login Host Protocol (TACACS) tacacs 49/udp re-mail-ck 50/tcp # Remote Mail Checking Protocol re-mail-ck 50/udp domain 53/tcp # name-domain server domain 53/udp mtp 57/tcp # deprecated tacacs-ds 65/tcp # TACACS-Database Service tacacs-ds 65/udp bootps 67/tcp # BOOTP server bootps 67/udp bootpc 68/tcp # BOOTP client bootpc 68/udp tftp 69/udp gopher 70/tcp # Internet Gopher gopher 70/udp rje 77/tcp netrjs finger 79/tcp www 80/tcp http # WorldWideWeb HTTP www 80/udp # HyperText Transfer Protocol ....snip....
Application Layer
DNS
HTTP
SSH